Dear Developers, in this article we will discuss about, how to create RESTful web services in Drupal 8 | 9.
This can be made possible by using HTTP requests to GET, PUT, POST and DELETE data. It is based on representational state transfer (REST) technology, an architectural style, and approach to communications often used in web services development.
With decoupled development getting the ground, it has become important for the developers to understand the REST technology better. Drupal provides its developers an in-house build method to use this REST technology. RESTful Web Services module, which is now a part of Drupal core, provides REST services to its developers.
Also, Read
- Drupal as a headless technology
- Install Drupal 9 using composer | install drupal 9 using composer with lando
- Create Drupal 9 Custom Module programatically
Let’s discuss step by step.
Step 1: Make sure for below points:
- install & Enable Rest UI Module
- Enable Basic Auth Module
Command for downloading Rest UI using composer.
lando composer require drupal/restui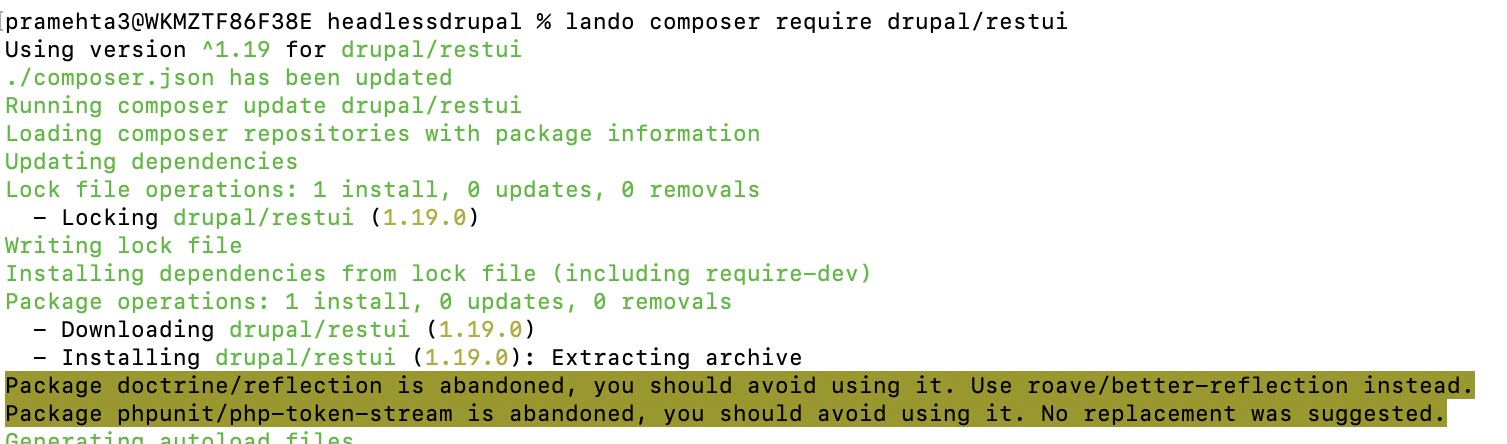
Enable module using drush
lando drush en restuiNote: it will ask for enabled it’s dependancy module, type yes and hit enter/return

Similarly, you can enable basic auth module, below is code for enable the basic auth module.
lando drush en basic_authNote: you can enable multiple modules at once using drush, just provide comma’s separated in commands. for details go to How to Download and Install Drupal 9 Modules
Step 2: You must have custom drupal 9 module, where you will write your Rest API, if you don’t have custom module create drupal 9 custom module development
Step 3: Create folder Plugin inside src. /Web/Modules/custom/your_custom_module_name/src/Plugin. Here /Web/Modules/custom/content_api/src/Plugin. If you don’t have such a folder directory or custom module then create.

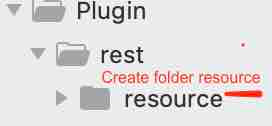
Step 4: Create folder rest inside Plugin: /Web/Modules/custom/content_api/src/Plugin/rest.

Step 5: Create folder resource inside rest. /Web/Modules/custom/content_api/src/Plugin/rest/resource.
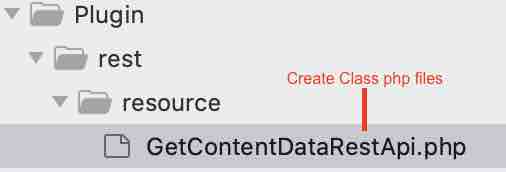
Step 6: Create API Class inside resource. /Web/Modules/custom/content_api/src/Plugin/rest/resource/GetContentDataRestApi.php.
Note: Drupal Rest api class name and file name both are must be same. Here file name is GetContentDataRestApi.php and it’s class name will be GetContentDataRestApi
Step 7: provide namespace of class and use some useful classes for drupal rest api on top of the file.
<?php
namespace Drupal\content_api\Plugin\rest\resource;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Url;
use Drupal\rest\Plugin\ResourceBase;
use Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\Exception\NotFoundHttpException;
use Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\Exception\BadRequestHttpException;
use Drupal\node\Entity\Node;
use Drupal\paragraphs\Entity\Paragraph;
use Drupal\rest\ModifiedResourceResponse;Step 8: Define annotation of classes, through which you can access Drupal 9 Rest API just after namespace and used class and above of class name.
/**
* Provides REST API for Content Based on URL.
*
* @RestResource(
* id = "get_content_rest_resource",
* label = @Translation("Content API"),
* uri_paths = {
* "canonical" = "/api/content"
* }
* )
*/Let’s understand annotation.
- it’s written inside commented code, just like above
- @RestResource is a function, through which know, it’s a kind of Rest Resource.
- id define the id of Rest Resource API
- label displaying to the user through which author can know about this api
- uri_paths : canonical attributes set the path of API.
Step 9: Define class name, make sure class name and php file name must be same, here file name is GetContentDataRestApi.php, so class name will be GetContentDataRestApi and it must be extends ResourceBase class
class GetContentDataRestApi extends ResourceBase { }Complete file will be like below
<?php
namespace Drupal\content_api\Plugin\rest\resource;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Url;
use Drupal\rest\Plugin\ResourceBase;
use Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\Exception\NotFoundHttpException;
use Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\Exception\BadRequestHttpException;
use Drupal\node\Entity\Node;
use Drupal\paragraphs\Entity\Paragraph;
use Drupal\rest\ModifiedResourceResponse;
/**
* Provides REST API for Content Based on URL.
*
* @RestResource(
* id = "get_content_rest_resource",
* label = @Translation("Content API"),
* uri_paths = {
* "canonical" = "/api/content"
* }
* )
*/
class GetContentDataRestApi extends ResourceBase {
/**
* Responds to entity GET requests.
*
* @return \Drupal\rest\ResourceResponse
* Returning rest resource.
*/
public function get() {
if (\Drupal::request()->query->has('url') ) {
$url = \Drupal::request()->query->get('url');
if (!empty($url)) {
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('field_unique_url', $url);
$nodes = $query->execute();
$node_id = array_values($nodes);
if (!empty($node_id)) {
$data = Node::load($node_id[0]);
return new ModifiedResourceResponse($data);
}
}
}
}
}
?>Step 10: To enable Rest API Go Configuration->Web Services->REST

Step 11: Search for content api which you have given in label and click on Enable button.
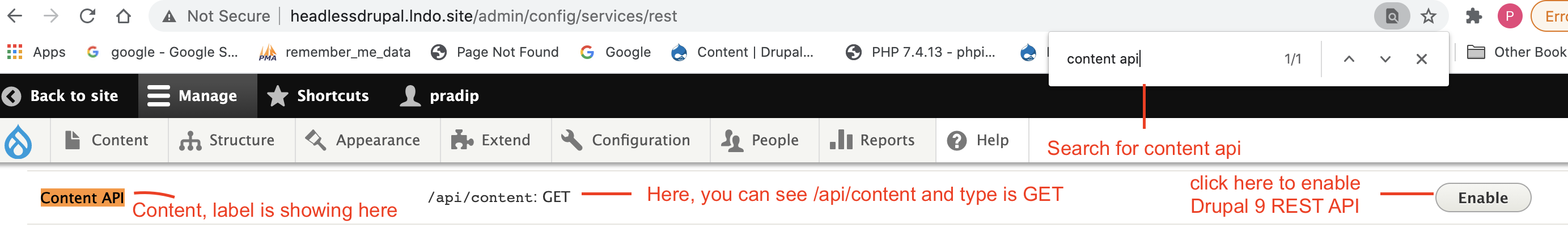
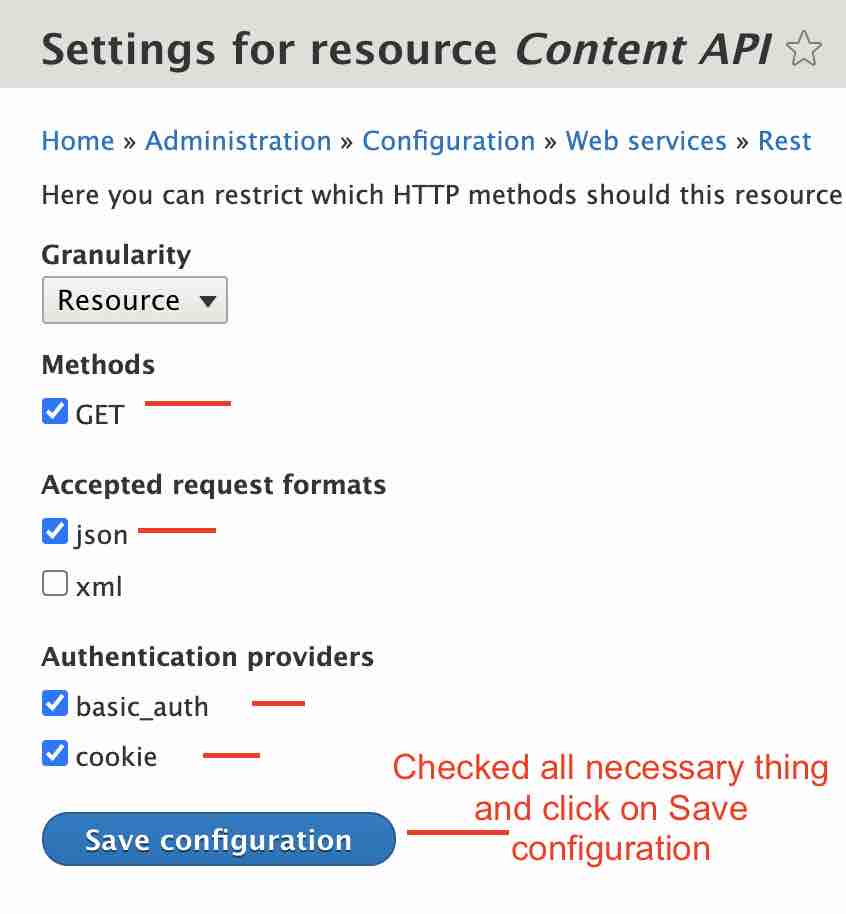
Step 12: click on Method GET and Accepted Request formats json and Authenticator providers basic auth and cookies and click on Save Configuration
Step 13: Create new drupal 9 content type, thought which we can make new template as per requirement. How to create content type in drupal 8 – 9
Step 14: Create node in this content type and provide Unique URL for all nodes though which we can access data as a REST API.
Step 15: you can hit your API using Postman or direct using URL: http://headlessdrupal.lndo.site/api/content?url=/testing
Let’s understand the above URL:
- http://headlessdrupal.lndo.site this is your domain name, mean base URL for your project.
- /api/content this is API canonical path or API
- ?url this is Parameter which we have defined in our API.
- /testing this is node Unique URL, this will be different for nodes.


